Kubectl Basic Commands
Kubectl Basic Commands
kubectl is the command-line tool used to interact with Kubernetes clusters. Here are some of the most commonly used commands:
1. kubectl get
The get command retrieves information about resources such as pods, services, deployments, etc.
Example:
kubectl get po
- If no namespace is specified, the default namespace is used.
- The following shows the
kubectl get pooutput in the default namespace: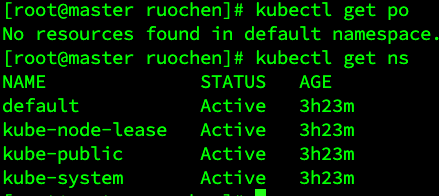
You can specify a namespace using the -n flag: kubectl get po -n <namespace>
2. kubectl scale
The scale command allows you to scale the number of replicas for a deployment or stateful set.
Example:
kubectl scale --replicas=5 deployment/my-deployment This command scales the my-deployment deployment to 5 replicas. Scaling up or down can be done by adjusting the --replicas value. 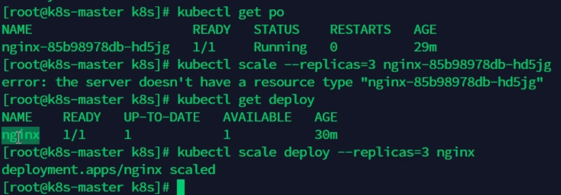
3. API Versions
Kubernetes has different API versions (e.g., beta, stable). Always try to use the stable version unless you need features available in beta.
Example of deprecated APIs:
To check the deprecation status of an API, refer to the Kubernetes Deprecation Guide.
For example, a deprecated API may look like: apiVersion: apps/v1beta1 # Deprecated version
Use the stable API version instead: apiVersion: apps/v1 # Stable version
Other Useful kubectl Commands:
kubectl describe <resource>: Get detailed information about a specific resource.kubectl logs <pod>: Fetch logs for a specific pod.kubectl apply -f <file.yaml>: Apply changes from a YAML file.
For more detailed information, refer to the official Kubernetes kubectl reference documentation.
