Setting up K3s Cluster on CentOS 9
November 7, 2024About 3 min
Setting up K3s Cluster on CentOS 9
Download mirror iso file on 'https://www.centos.org/download/', and use VMWare Fusion to set up 3 different CentOS 9.
This guide will walk you through setting up a K3s cluster with 1 master node and 2 worker nodes on CentOS 9. The master node's IP is 172.16.217.137, worker nodes' IPs are 172.16.217.138 and 172.16.217.139.
Key Kubernetes Components
1. kubeadm - Cluster Initialization Tool
- Purpose:
kubeadmis designed for setting up and configuring a Kubernetes cluster. It helps users quickly establish a standardized Kubernetes environment. - Functions:
- Initializes the main cluster components, such as the API server, scheduler, and controllers.
- Generates configuration files and certificates, enabling secure communication within the cluster.
- Configures network plugins for inter-Pod communication.
- Manages node addition and removal within the cluster.
- Use Case:
kubeadmis ideal for initializing and joining multiple nodes to create a production or development Kubernetes cluster.
2. kubectl - Cluster Management Tool
- Purpose:
kubectlis the command-line tool for interacting with Kubernetes, allowing users to manage and operate cluster resources. - Functions:
- Manages Kubernetes resources, including creating, updating, and deleting Pods, Services, Deployments, and more.
- Provides real-time cluster insights and retrieves node and container status information.
- Configures and manages Kubernetes resources like scheduling, volumes, and networking.
- Supports debugging and logging with commands to view container logs or access container shells.
- Use Case:
kubectlis essential for administrators and developers for managing and controlling Kubernetes resources within a cluster.
3. kubelet - Core Node Agent
- Purpose:
kubeletis a crucial component that runs on each node, responsible for managing the lifecycle of containers and Pods on that node. - Functions:
- Communicates with the Kubernetes API server to receive Pod assignments for the node.
- Manages container lifecycle through container runtimes (e.g., Docker or containerd).
- Regularly reports node and container status to the API server, ensuring the cluster has up-to-date resource information.
- Oversees node health and resources, monitoring and reporting resource usage.
- Use Case:
kubeletis the core process ensuring that Pods assigned to a node operate reliably, making it essential for resource scheduling and container management.
Why using K3s?
K3s - Lightweight Kubernetes Distribution
K3s is a simplified and lightweight distribution of Kubernetes that incorporates the core functionalities of kubeadm, kubectl, and kubelet. Developed for resource-constrained environments and edge computing, K3s significantly reduces the complexity of installing and maintaining a Kubernetes cluster.
Key Benefits of K3s:
- Integrated Core Features: K3s includes the essential features of
kubeadm,kubectl, andkubelet, providing a streamlined installation process. - Lightweight and Resource-Efficient: Designed to run on resource-limited devices (e.g., ARM64, Raspberry Pi), K3s is ideal for edge computing, IoT, and minimal hardware environments.
- Reduced Overhead: With built-in networking, container runtimes, and streamlined configuration, K3s simplifies Kubernetes setup and management, making it easy to deploy clusters in constrained environments.
Summary
kubeadm: Initializes and configures clusters, facilitating node addition.kubectl: Manages and operates Kubernetes resources.kubelet: Manages container lifecycle on each node, ensuring Pods function correctly.
K3s integrates the essential functions of these tools, providing a lightweight and accessible Kubernetes solution suitable for environments with limited resources.
1. Install K3s on Master Node
On the master node (172.16.217.137), run the following command to install K3s:
curl -sfL https://get.k3s.io | sh -Once K3s is installed, configure the kubeconfig file to allow access to the Kubernetes cluster from your local machine:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/rancher/k3s/k3s.yaml $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config2. Get the K3s Join Token
To add worker nodes to the cluster, you need the K3s join token. On the master node, run:
sudo cat /var/lib/rancher/k3s/server/node-tokenCopy the output token for use on the worker nodes.
3. Install K3s on Worker Nodes
On each worker node (172.16.217.138 and 172.16.217.139), run the following command to install K3s and join the cluster:
For Node1 (172.16.217.138):
curl -sfL https://get.k3s.io | K3S_URL=https://172.16.217.138:6443 K3S_TOKEN=<MASTER_NODE_TOKEN> sh -For Node2 (172.16.217.139):
curl -sfL https://get.k3s.io | K3S_URL=https://172.16.217.139:6443 K3S_TOKEN=<MASTER_NODE_TOKEN> sh -Make sure to replace <MASTER_NODE_TOKEN> with the token obtained from the master node.
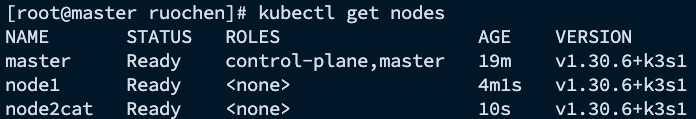
4. Verify Cluster Status
Back on the master node, verify that the worker nodes have successfully joined the cluster:
kubectl get nodes
You should see output similar to: